Magnetic Sensing Systems
Magnetic sensing is an emerging sensing modality with unique advantages: fine granularity, high resilience, efficiency, and low cost.
Kickstarted in 2021, our works have been inventing magnetic sensing technologies that can be used for tackling pressing real-world challenges, e.g., motion capture and intelligent roads.
PI: Dongyao Chen
DemoResearch updates
Please check out our latest works here:
- [MobiCom' 21] Wearable, untethered hands tracking with passive magnets
- [MobiCom' 22] Automatic Calibration of Magnetic Tracking
- [SenSys' 23] METRO: Magnetic Road Markings for All-weather, Smart Roads
- [UbiComp' 24] MagDot: Drift-free, Wearable Joint Angle Tracking at Low Cost
- [MobiCom' 24] Polaris: Accurate, Vision-free Fiducials for Mobile Robots with Magnetic Constellation
Phase 3. Advancing High Wearability with MagDot

Tracking joint movement is crucial for a range of applications, including virtual/augmented reality, sports monitoring, and medical rehabilitation. However, existing technologies like cameras, IMUs, and flex sensors often fall short due to issues like occlusion, cumulative error, and high costs, which limit their practicality for joint tracking. MagDot stands out by offering high-accuracy, drift-free, and wearable joint angle tracking. It employs a unique tracking scheme that effectively compensates for various real-world challenges, ensuring accurate and reliable performance. Test results revealed MagDot's capability to track major body joints precisely, with an accuracy of 2.72° for the elbow, 4.14° for the knee, and 4.61° for the shoulder. MagDot only incurs 98 mW power consumption, enabling full-day operation on a small battery pack. Each MagDot unit costs less than $35.
Phase 2. Enhancing Reliability with MAGIC Calibration

Magnetic tracking, with its applications in posture tracking, human-machine interaction, and haptic sensing, relies on MEMS magnetometers to detect changes in magnetic fields. However, a significant challenge in this technology is its sensitivity to real-world disturbances, including hard- and soft-iron effects. These disturbances can be incurred by everyday objects such as smartphone, earphone, and even metal furniture. These disturbances traditionally require users to undertake a frequent, cumbersome calibration process, impacting the practicality of magnetic tracking. We introduced MAGIC (MAGnetometer automatIc Calibration), a comprehensive framework designed to automatically calibrate both soft- and hard-iron disturbances in MEMS magnetometer arrays. A key innovation of MAGIC is its novel auto-triggering module, which minimizes user involvement compared to traditional manual calibration methods. This feature allows MAGIC to achieve enhanced calibration accuracy with minimal user effort.
Phase 1. Embedded magnetic tracking with MagX

Traditional methods, such as instrumented gloves or vision-based systems, often hindered by line-of-sight occlusions, bulkiness, or privacy concerns, restricting their practical use in real-world applications. MagX offers a fully untethered, accurate, and wearable hand-tracking solution using passive magnets and an innovative magnetic sensing array. Since passive magnets require no maintenance, they can be worn on the hands indefinitely, and only the sensor board needs recharging, akin to a smartwatch. Our experiments with MagX have demonstrated millimeter-level accuracy in 5 DoF tracking of two independent magnets. For instance, with a 6cm × 6cm sensing array at 11 cm distance, we achieved positional and orientational errors of just 0.76 cm and 0.11 rad, respectively. At greater distances, like 21 cm, the errors are marginally higher, at 2.65 cm and 0.41 rad. MagX is highly energy-efficient, performing all computations locally and requiring just 0.38 W total power. This efficiency allows for extended, “all day” operation on a battery the size of a typical smartwatch. The MagX system's compact form factor, accuracy, and low power consumption make it a promising candidate for widespread adoption in diverse applications, from high-precision VR interaction to tracking in-vivo endocapsule.
Phase X. Advancing Road Safety with Magnetic Sensing
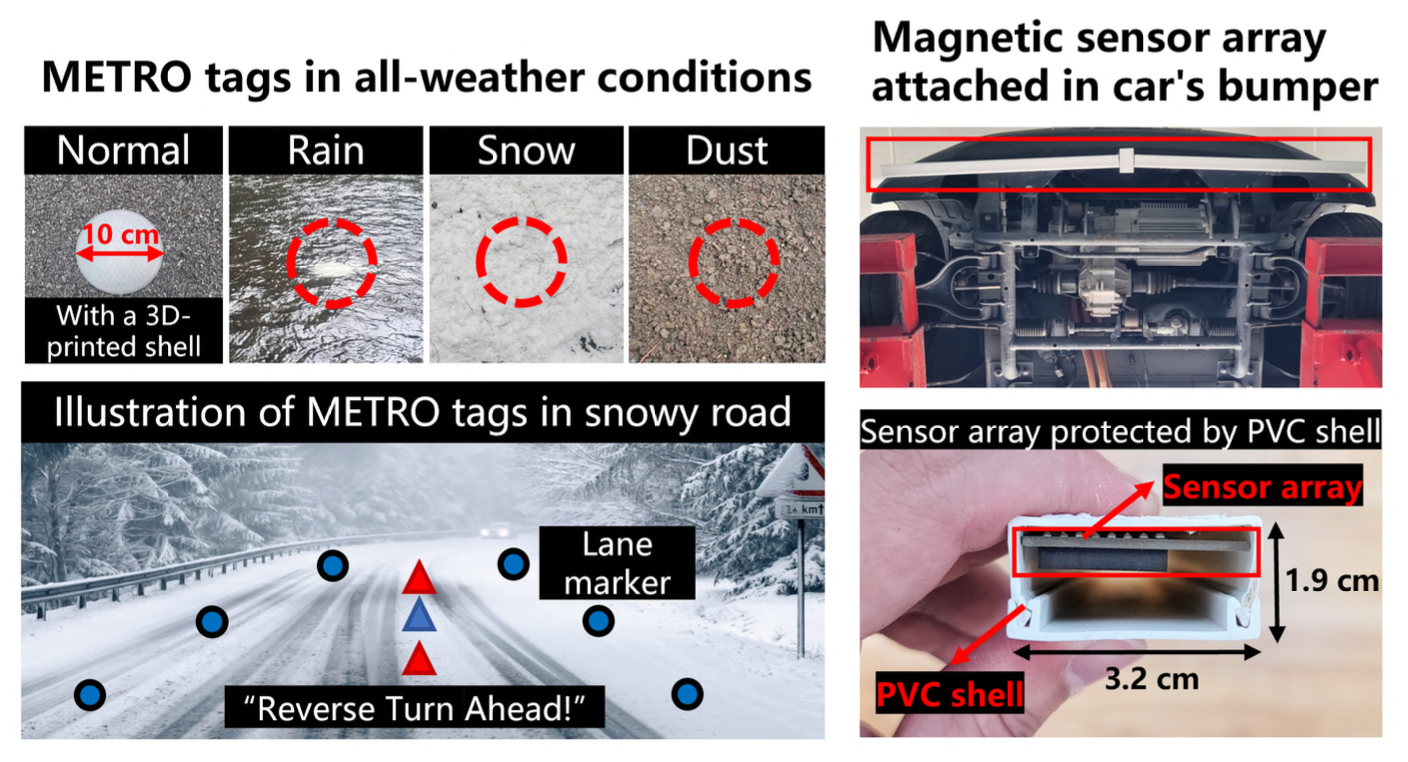
MagnETic ROad marking system (METRO) is a novel approach combining passive magnetic markers with an advanced automotive-grade magnetic sensing framework. METRO is engineered to mitigate the effects of magnetic disturbances, reduce deployment costs significantly, and enhance the longevity of road markers. Comprehensive field tests have demonstrated METRO's remarkable accuracy and cost-effectiveness. The system consistently identified various road markings with over 96% accuracy in diverse weather conditions at a substantially lower cost (about $0.17 per meter) compared to conventional road markings (which range from $0.21 to $7.70 per meter). The magnetic tag survived a 6-month on-road test. The sensor array performed consistently throughout the testing period, underscoring METRO's potential as a resilient and cost-efficient solution for all-weather road safety. The complete repository of METRO can be found online.
Yes, we open sourced our projects
We are committed to open source research. Please find our code bases below.