MagDot: Drift-free, Wearable Joint Angle Tracking at Low Cost
Dongyao Chen, Qing Luo, Xiaomeng Chen, Xinbing Wang, Chenghu Zhou
Paper Accepted by UbiComp 2024
Targeted Problem

Tracking the angular movement of body joints has been a critical enabler for various applications, such as virtual and augmented reality, sports monitoring, and medical rehabilitation. Despite the strong demand for accurate joint tracking, existing techniques, such as cameras, IMUs, and flex sensors, suffer from major limitations that include occlusion, cumulative error, and high cost. These issues collectively undermine the practicality of joint tracking.
Technology
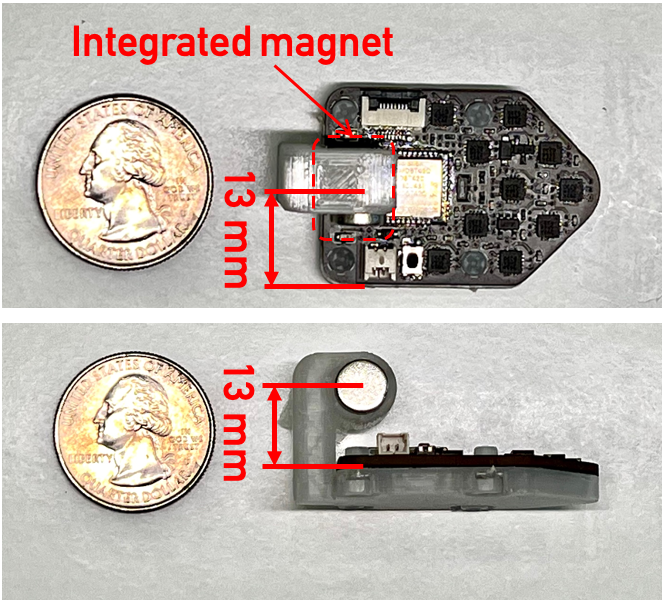
Overview
We introduce MagDot, a new magnetic-based joint tracking method that enables high-accuracy, drift-free, and wearable joint angle tracking. To overcome the limitations of existing techniques, MagDot employs a novel tracking scheme that compensates for various real-world impacts, achieving high tracking accuracy.
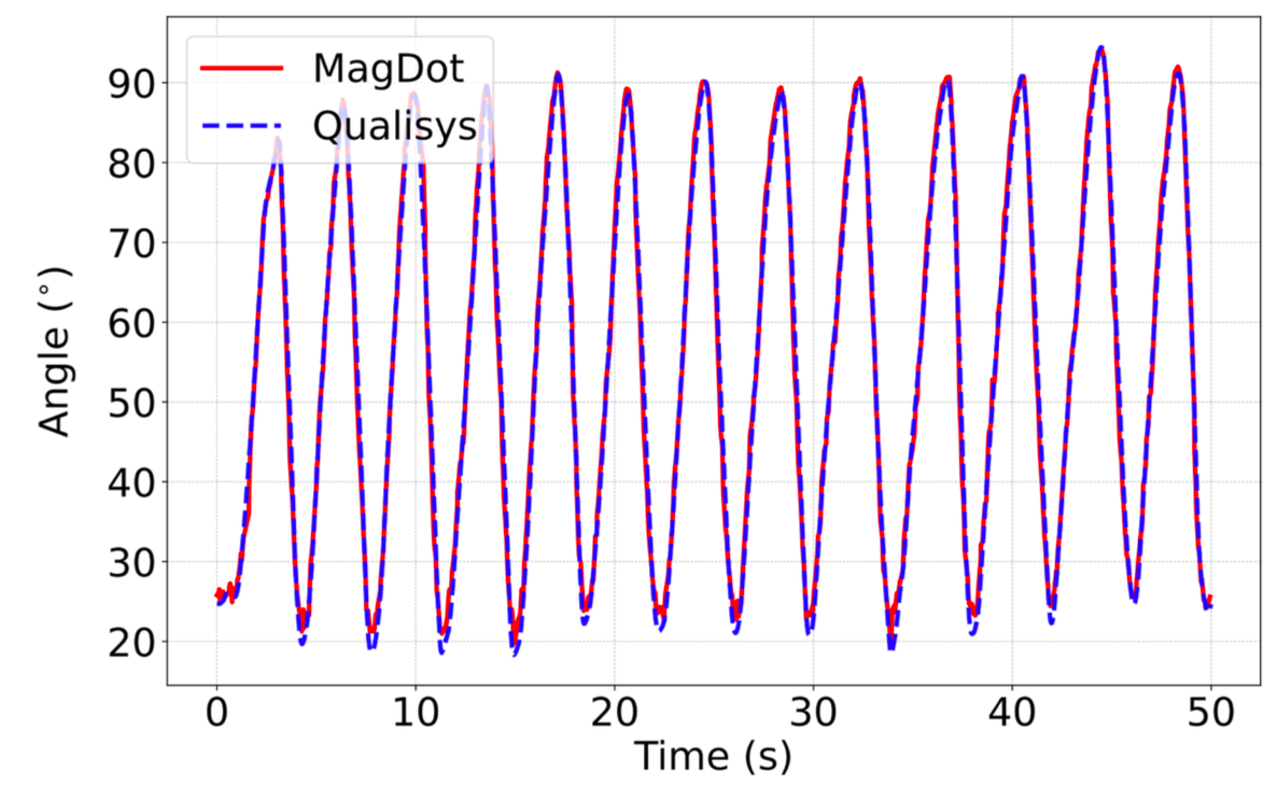
Performance
We tested MagDot on eight participants with a professional motion capture system, i.e., Qualisys motion capture system with nine Arqus A12 cameras. The results indicate MagDot can accurately track major body joints. For example, MagDot can achieve tracking accuracy of 2.72◦ , 4.14◦, and 4.61◦ for elbow, knee, and shoulder, respectively. With a power consumption of only 98 𝑚𝑊, MagDot can support one-day usage with a small battery pack.
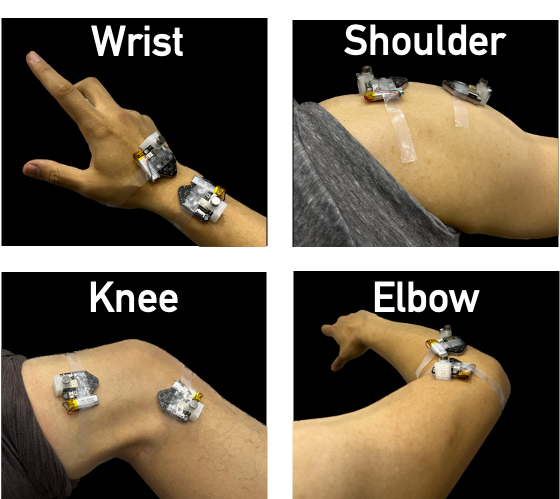
Application
MagDot units can be attached to different types of joints, e.g., wrist, shoulder, knee, and elbow. By sensing the relative position between two units, MagDot system can accurately measure joint angles. It can be used for various motion sensing applications such as analyzing the shoot form for basketball training.
Open source
Yes, MagDot will be open for research purpose, we are actively pushing this progress. For more questions, please contact us.
Cite Our Work
Dongyao Chen, Qing Luo, Xiaomeng Chen, Xinbing Wang, and Chenghu Zhou. 2024. MagDot: Drift-free, Wearable Joint Angle Tracking at Low Cost. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 7, 4, Article 150 (December 2023), 25 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3631423