Assistant Professor, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Sensing Intelligence & System Lab (SISL)
I am an Assistant Professor in Computer Science at Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU). I obtained my Ph.D. (2020) in Computer Science and Engineering from the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. I was fortunate to have Prof. Kang G. Shin as my advisor. I lead the Sensing Intelligence & System Lab (SISL) at SJTU. You can always find our latest demos here.
Mission Statement
In today's rapidly changing technology landscape, we are poised to land on Mars and build intelligence that can surpass us. Yet, our technologies still severely fall short in understanding ourselves. For example, analyzing our everyday motion with high accuracy and quantifying our habits. Sometimes even our step counter is not accurate!
At SISL, we bridge this gap between ourselves and machines by building human-centered sensing systems. Our works not only empower individuals to better understand and improve their mobility, safety, and well-being, but also fuel innovations in broader domains like autonomous driving and robotics.
Recent News
- Feb. 2026, MagLens got accepted by SenSys 2026! Congratuations to Jike and the team!.
- Jan. 2026, microTouch got accepted by PerCom 2026! Congratuations to Siyuan and the team!.
- Oct. 2025, DualStrike got accepted by NDSS 2026! For the first time, we demonstrated the vulnerability of magnetic sensing platforms. Congratuations to Xiaomeng and the team!.
- Jun. 2025, I will be serving as the Student Travel Grant co-chair for MobiCom 2025, apply here.
- Apr. 2025, BRIDGE is accepted by MobiCom 2025.
- Nov. 2024, MagDesk is accepted by UbiComp. Congrats to the team work! Check out our demo here. Kunpeng will debut MagDesk at UbiComp 2025 at Finland!
- Sept. 2024, I will be serving in the TPC for MobiCom 2025. Please consider submitting your best work!
- Aug. 2024, delighted to present "Enabling Magnetoreception for Cyber-Physical Systems" at NUS, NTU, and SMU!
- Jun. 2024, Polaris is accepted by MobiCom 2024! Check out our demo here. We are excited about the next step of magnetic sensing!
- Dec. 2023, MagDot is accepted by UbiComp 2024! MagDot introduces the world's first drift-free, low-cost joint angle sensing platform!
- Oct. 2023, METRO is accepted by SenSys 2023. This is the first paper by my student Jike! METRO demonstrated how magnetic sensing can make our roads safer!
- Sept. 2023, I will be serving in the TPC for MobiCom 2024.
- Mar. 2023, VeFi received the Best Paper Award at the Inaugural ISOC Symposium on Vehicle Security and Privacy (VehicleSec 2023)!
Research works at SISL
At SISL, we build new technologies for solving real-world problems. Exemplary usage scenarios fall in smart transportation and healthcare. For prospective students, we are actively looking for self-motivated new members. If you are interested in the following topics, please drop me an email!
Publications
(Underlined authors are my direct advisees, '*' denotes co-primary authors)
μTouch: Enabling Accurate, Lightweight Self-Touch Sensing with Passive Magnets
PerCom 2026Siyuan Wang, Ke Li, Jingyuan Huang, Jike Wang, Cheng Zhang, Alanson Sample, and Dongyao Chen
Self-touch gestures (e.g., nuanced facial touches and subtle finger scratches) provide rich insights into human behaviors, from hygiene practices to health monitoring. μTouch presents a novel magnetic sensing platform for self-touch gesture recognition.
Paper (Coming soon)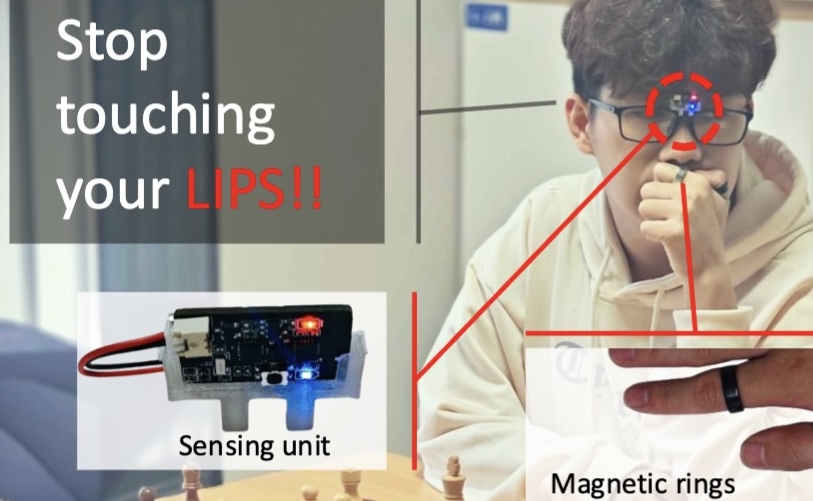
DualStrike: Accurate, Real-time Eavesdropping and Injection of Keystrokes on Commodity Keyboards
NDSS 2026Xiaomeng Chen, Jike Wang, Zhenyu Chen, Qi Alfred Chen, Xinbing Wang, and Dongyao Chen
To the best of our knowledge, DualStrike is the first attack scheme that can simultaneously listening and injecting to commodity keyboards.
Paper | Project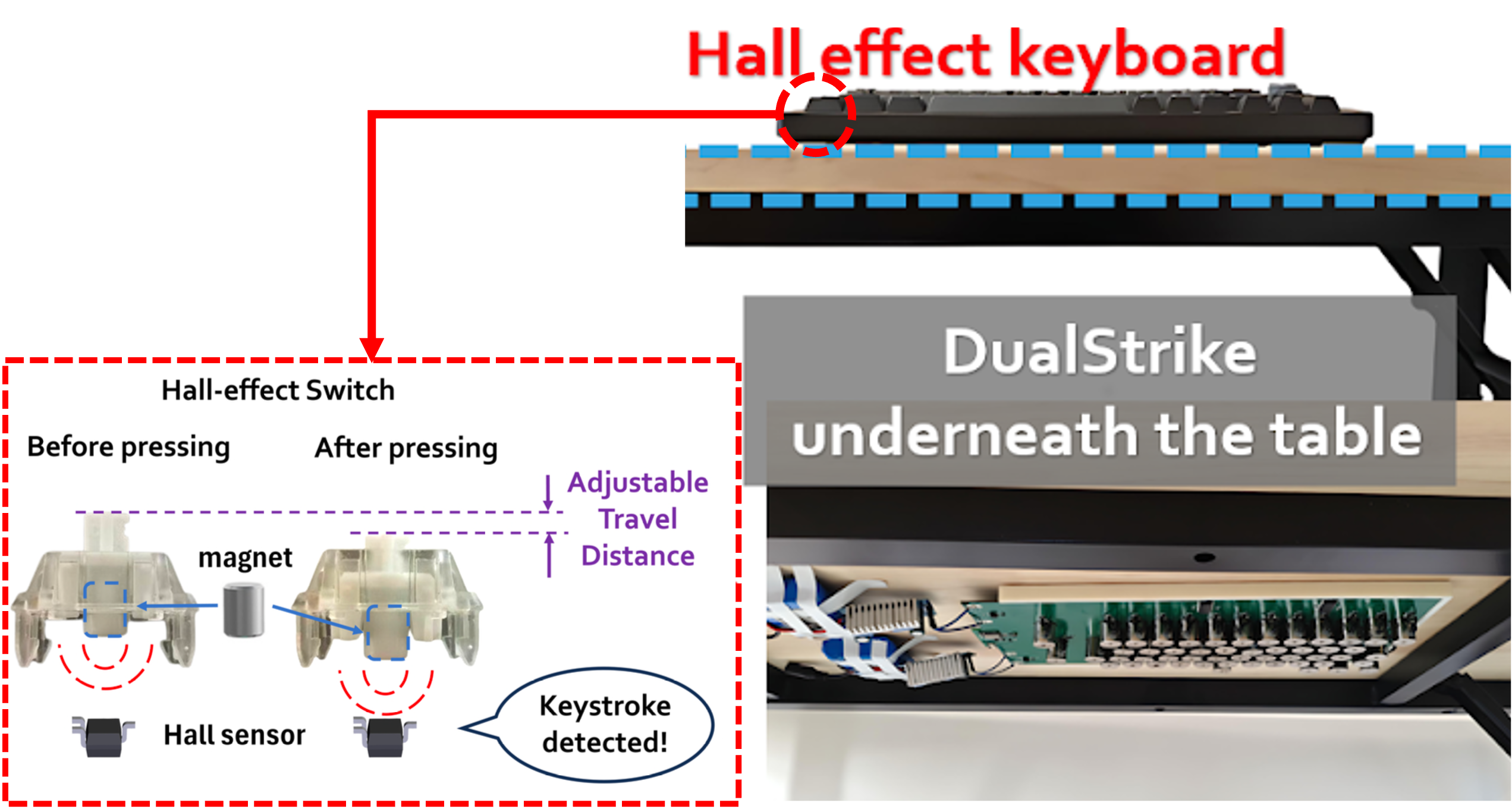
Towards Extended Interaction with Differential Magnetic Tracking and Deep Learning
IJHCI 2025Zhenyu Chen, Peihang Chen, Jingyuan Huang, and Dongyao Chen
Our approach overcomes the initial parameter settings of LM algorithm, thus expanding magnetic sensing's usability for mobile scenarios.
Paper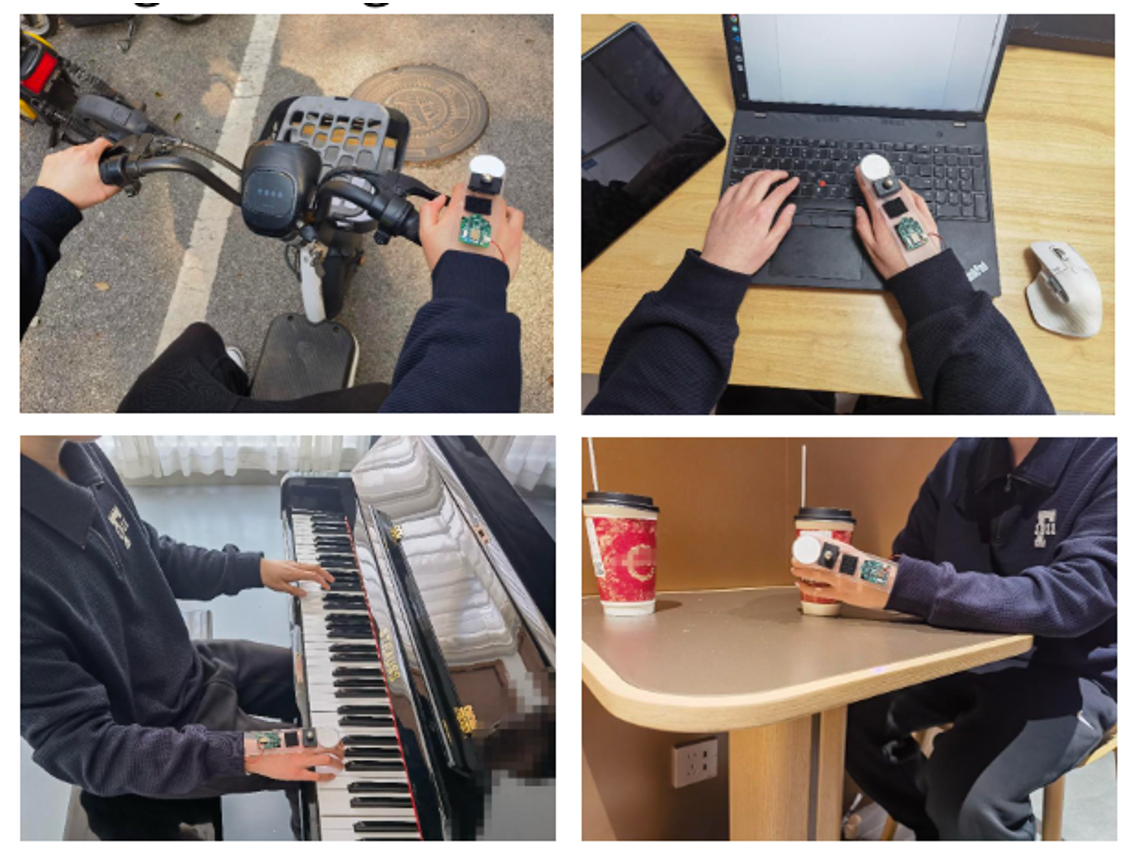
Bridge: Enabling BLE Direction Finding Feature Compatible with All Bluetooth Devices
MobiCom 2025Runting Zhang, Yijie Li, Dian Ding, Yi-Chao Chen, Yida Wang, Dongyao Chen, Jingxian Wang, Jiadi Yu, Ling Ma, Guangtao Xue
BRIDGE offers backward compatability of the direction finding feature, exclusive to BLE v5.1, with other BLE devices.
Paper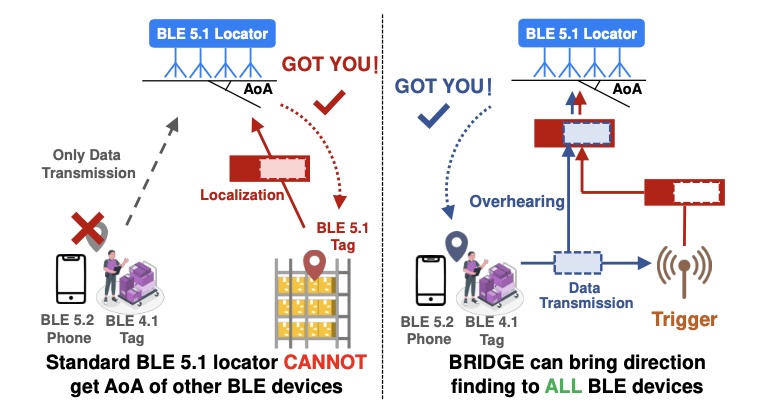
MagDesk: Interactive Tabletop Workspace Based on Passive Magnetic Tracking
UbiComp 2025 ( Distinguished Paper Award)Kunpeng Huang, Yasha Iravantchi, Dongyao Chen, and Alanson Sample
This paper introduces MagDesk, an interactive tabletop workspace capable of real-time 3D tracking of passive magnets embedded in objects.
Paper | Demo
Polaris: Accurate, Vision-free Fiducials for Mobile Robots with Magnetic Constellation
MobiCom 2024Jike Wang, Yasha Iravantchi, Alanson Sample, Kang G. Shin, Xinbing Wang, Dongyao Chen
Fiducial tags are essential for robots. They provide crucial supports such as pose calibration, contextual perception, and navigation. In Polaris, we build the world first invisible fiducial tag with magnetic sensing.
Paper | Code | Demo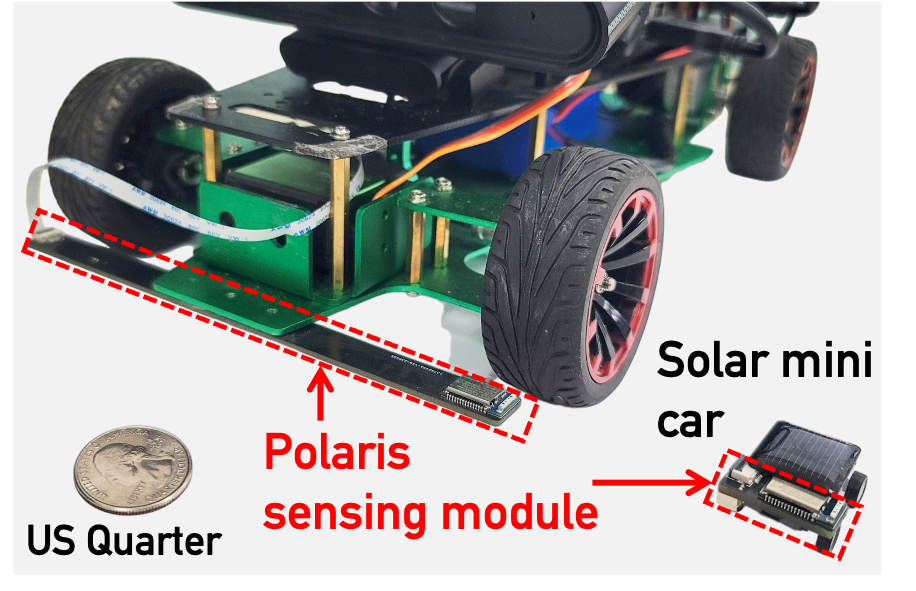
MagDot: Drift-free, Wearable Joint Angle Tracking at Low Cost
UbiComp 2024Dongyao Chen, Qing Luo, Xiaomeng Chen, Xinbing Wang, Chenghu Zhou
Tracking the angular movement of body joints has been a critical enabler for various applications, such as virtual and augmented reality, sports monitoring, and medical rehabilitation. MagDot is the first wearable system that achieves drift-free joint tracking. Experiment results indicate MagDot can achieve tracking accuracy of 2.72◦, 4.14◦, and 4.61◦ for elbow, knee, and shoulder, respectively.
Paper | Website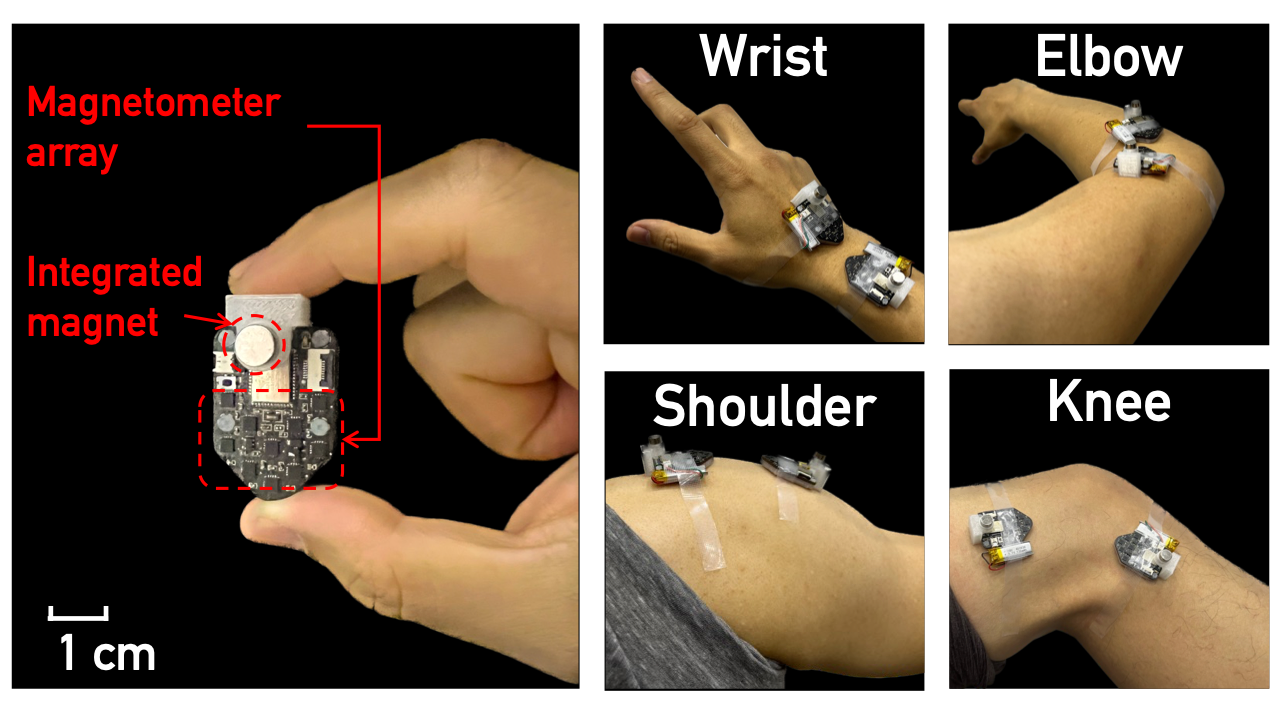
Implementation and Benchmark of Magnetic Tracking on Mobile Platforms
AIoTSys (Co-hosted with MobiSys 2024)Zhenyu Chen, Jike Wang, and Dongyao Chen
We demonstrate the deployment of magnetic tracking techniques on commodity smartphones. Our implementation is benchmarked on a Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) Android smartphone. Empirical studies indicate that our implementation on mobile platforms is both energy-efficient and highly effective.
Paper | Code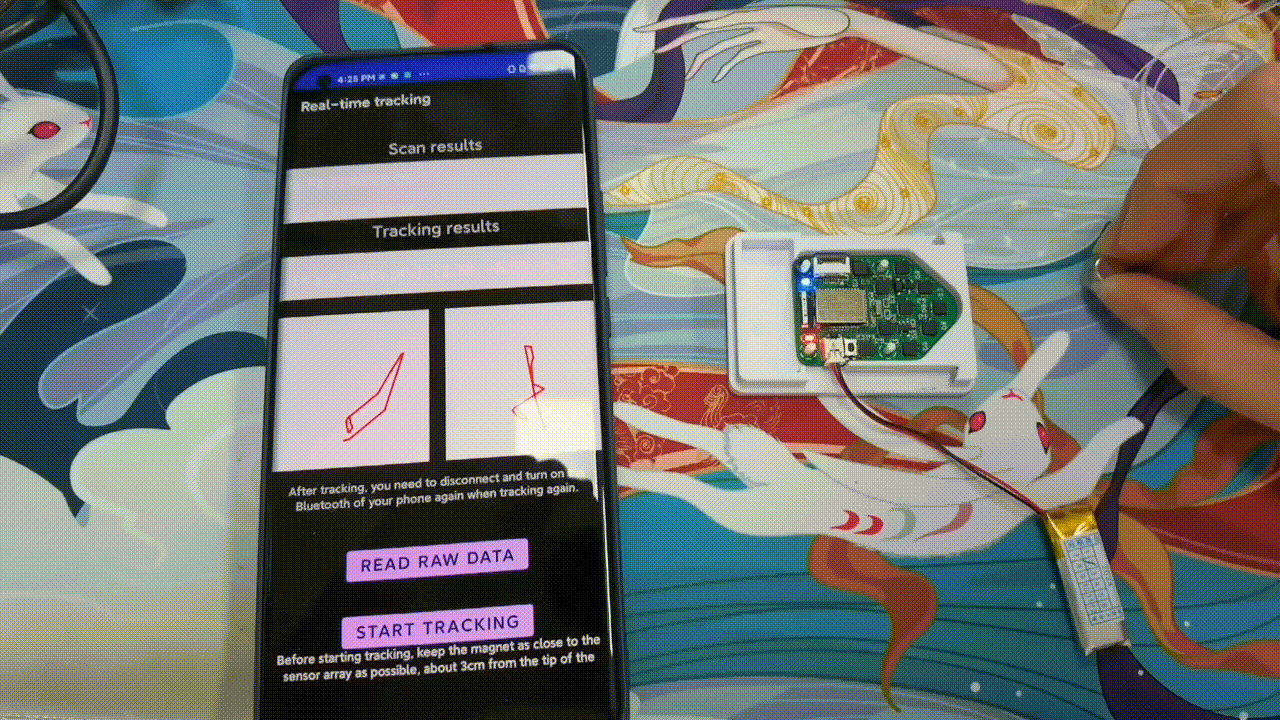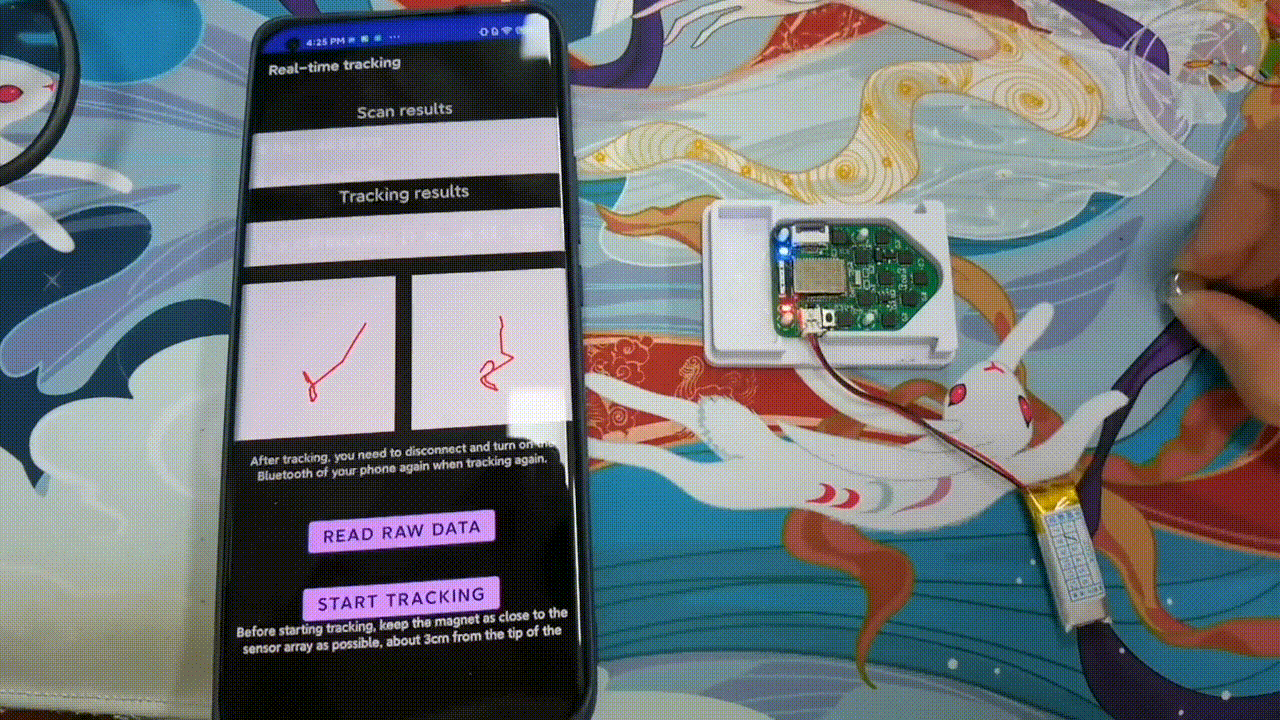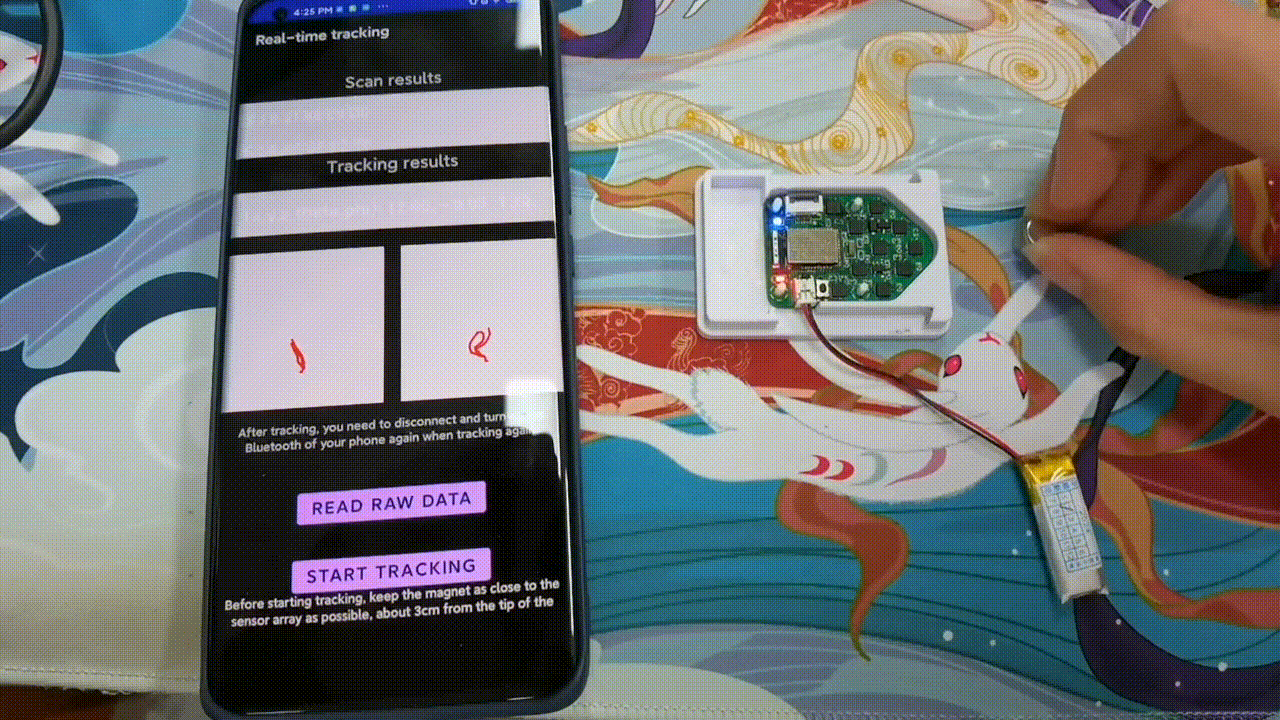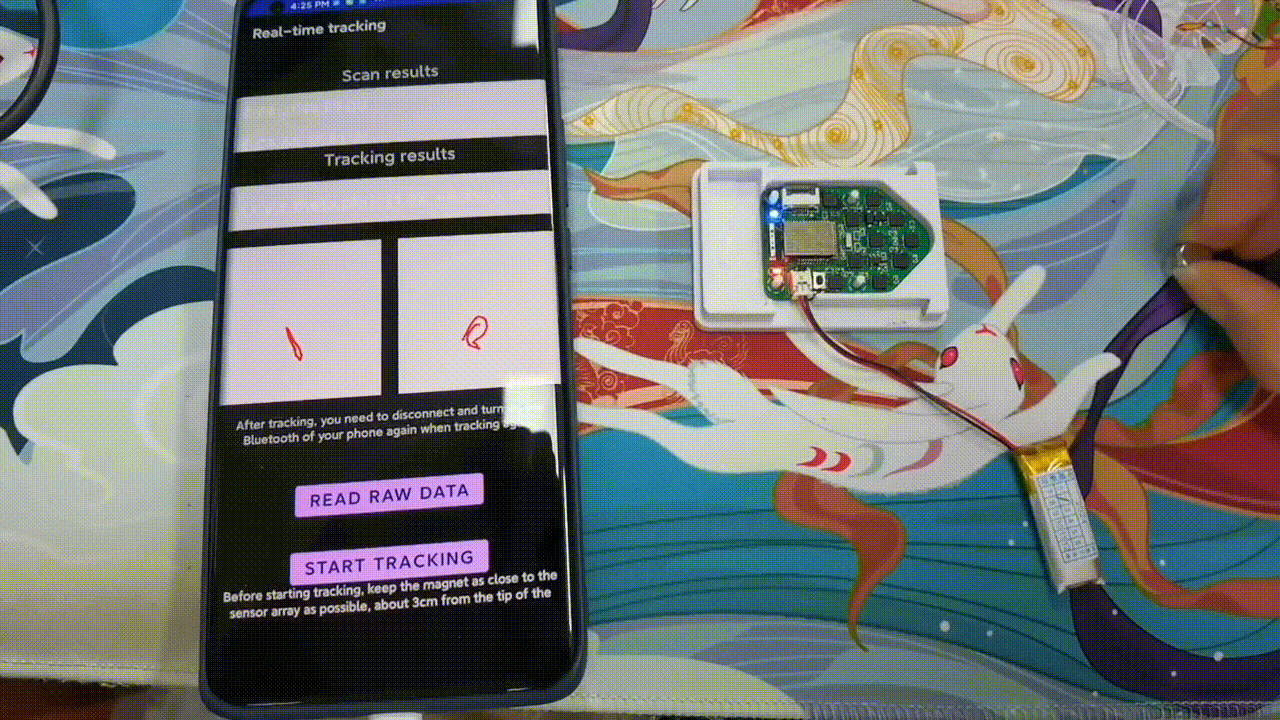
METRO: Magnetic Road Markings for All-weather, Smart Roads
SenSys 2023Jike Wang, Shanmu Wang, Yasha Iravantchi, Mingke Wang, Alanson Sample, Kang G. Shin, Xinbing Wang, Chenghu Zhou, Dongyao Chen
Allowing cars to "see" road markings is crucial for traffic safety. However, road markings, e.g., lanes and pedestrian crossings, can be easily occluded by bad weather. METRO proposed a novel magnetic sensing approach to encode rich information with passive magnets. METRO is tested and verified on REAL-WORLD ROADS!
Paper | Code | Slides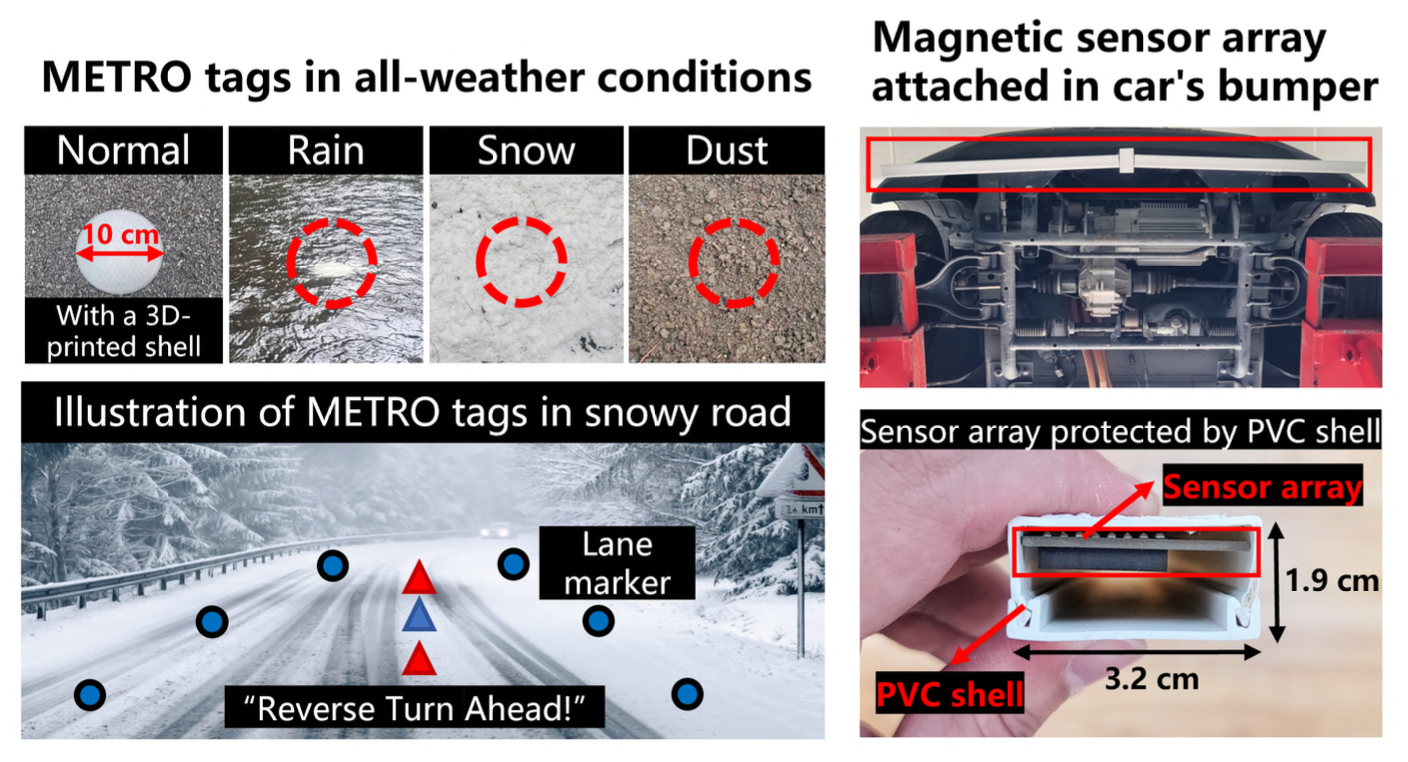
Guess Which Car Type I Am Driving: Information Leak via Driving Apps
VehicleSec 2023 ( Best Paper Award)Dongyao Chen, Mert D. Pesé, and Kang G. Shin
We leveraged the widely available smartphone data to infer the vehicle type information.
Paper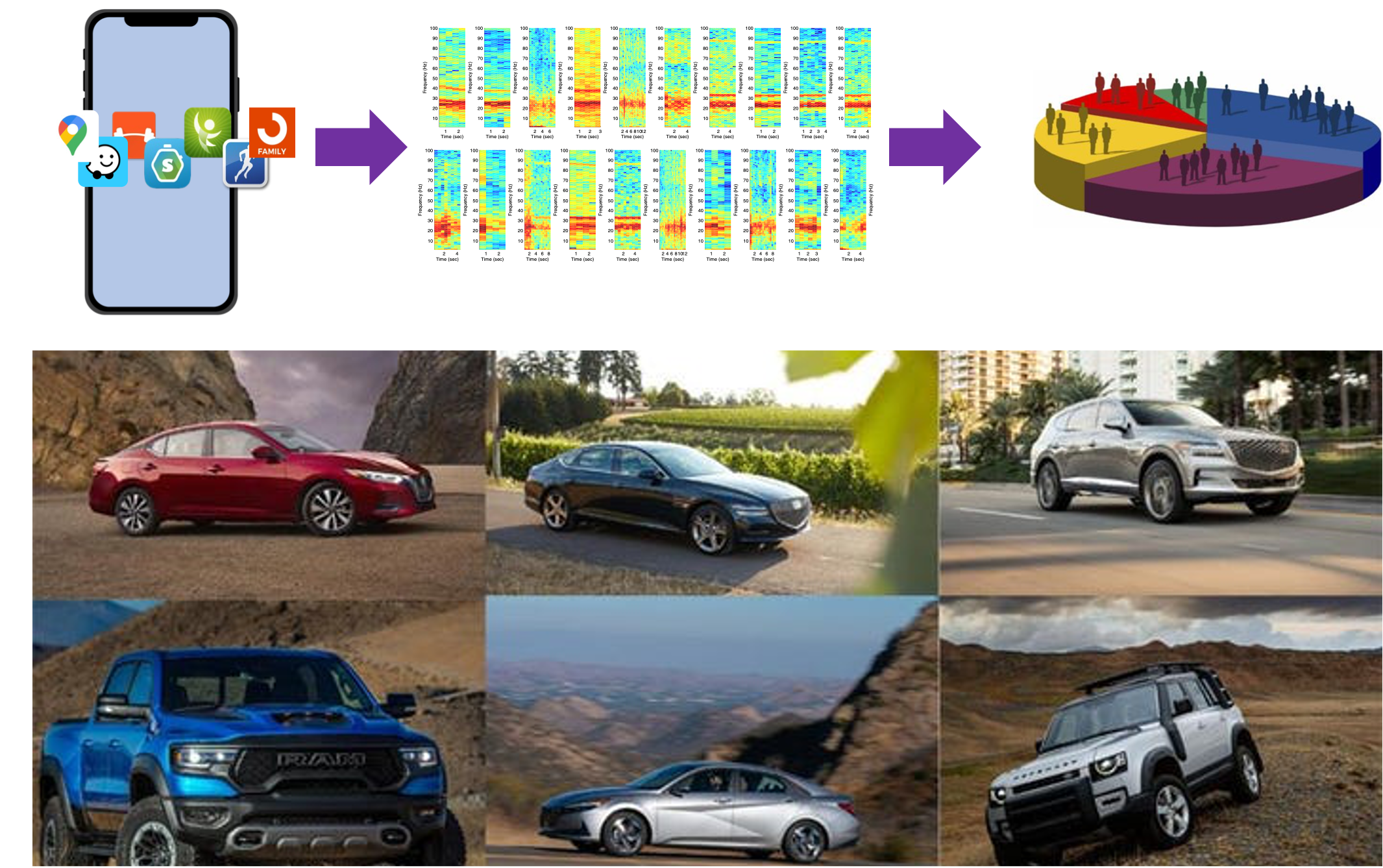
Automatic Calibration of Magnetic Tracking
MobiCom 2022Mingke Wang*, Qing Luo*, Yasha Iravantchi, Xiaomeng Chen, Alanson Sample, Kang G. Shin, Xiaohua Tian, Xinbing Wang, Dongyao Chen
We proposed MAGIC, a systematic framework to automatically calibrate both soft- and hard-iron disturbances for a MEMS magnetometer array.
Paper | Demo | Slides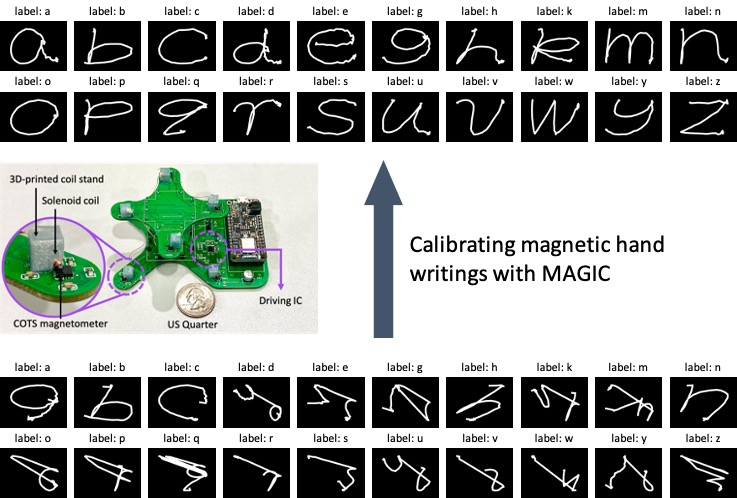
Enabling Software-defined PHY for Backscatter Networks
MobiSys 2022Fengyuan Zhu, Mingwei Ouyang, Luwei Feng, Yaoyu Liu, Xiaohua Tian, Meng Jin, Dongyao Chen, Xinbing Wang
In this work, we for the first time show how to enable softwaredefined PHY (SD-PHY) to achieve agile reprogrammability in wireless backscatter networks. This can facilitate innovations in this field by relieving researchers from unnecessary engineering work.
Paper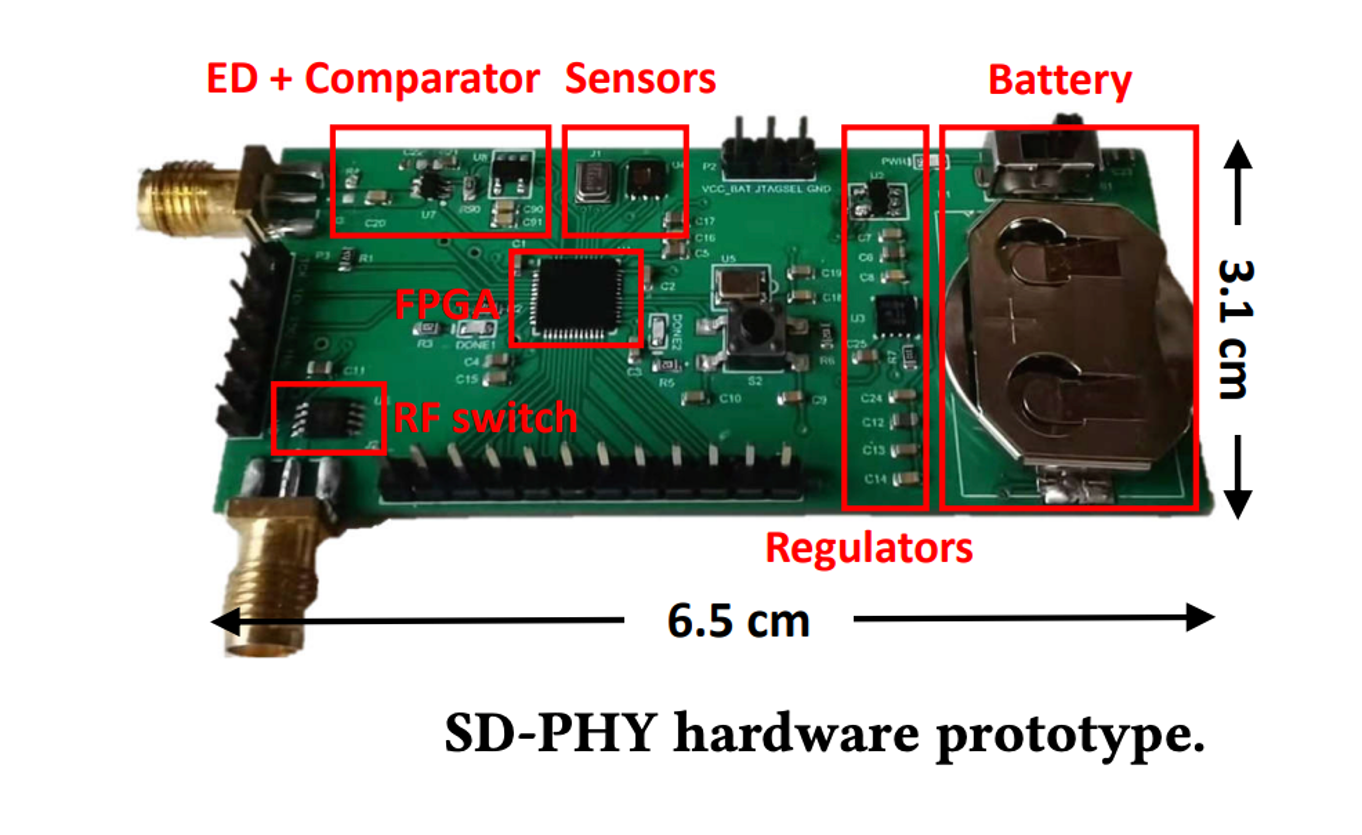
DETROIT: Data Collection, Translation and Sharing for Rapid Vehicular App Development
SECON 2022Mert D. Pesé, Dongyao Chen, C. Andrés Campos, Alice Ying, Troy Stacer, Kang G. Shin
DETROIT is an open-source vehicle-agnostic end- to-end framework for vehicular data collection, translation and sharing that facilitates the rapid development of automotive apps.
Paper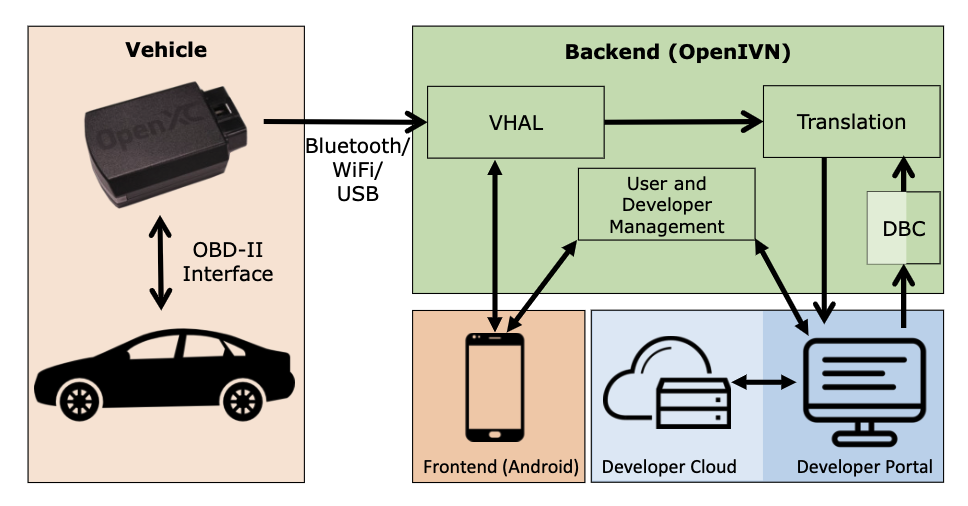
MagX: Wearable, Untethered Hands Tracking with Passive Magnets
MobiCom 2021Dongyao Chen, Mingke Wang, Chenxi He, Qing Luo, Yasha Iravantchi, Alanson Sample, Kang G. Shin, Xinbing Wang
We proposed MagX, the first untethered and mobile magnetic tracking platform for fine-grained hand tracking. Exemplary applications includes AR/VR interaction and face-touching detection.
Paper | Code | Slides | Website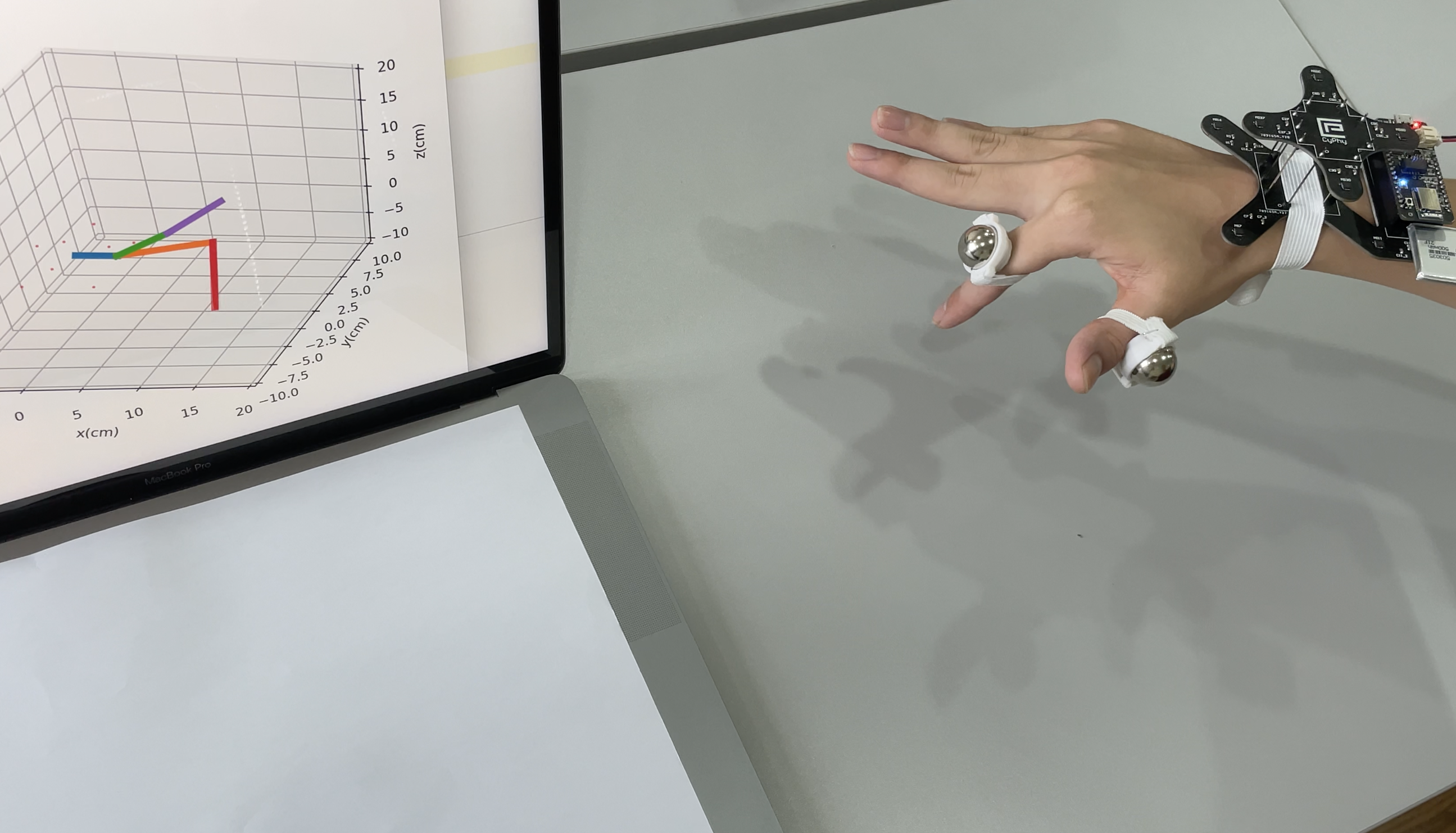
Authenticating Drivers Using Automotive Batteries
UbiComp 2021Liang He, Yuanchao Shu, Youngmoon Lee, Dongyao Chen, Kang G. Shin
This work presented B-Auth, a vehicle battery-based driver authentication platform. We discovered the connection between battery voltage with the driver's behavior, e.g., braking, acceleration, using wipers, etc.
Paper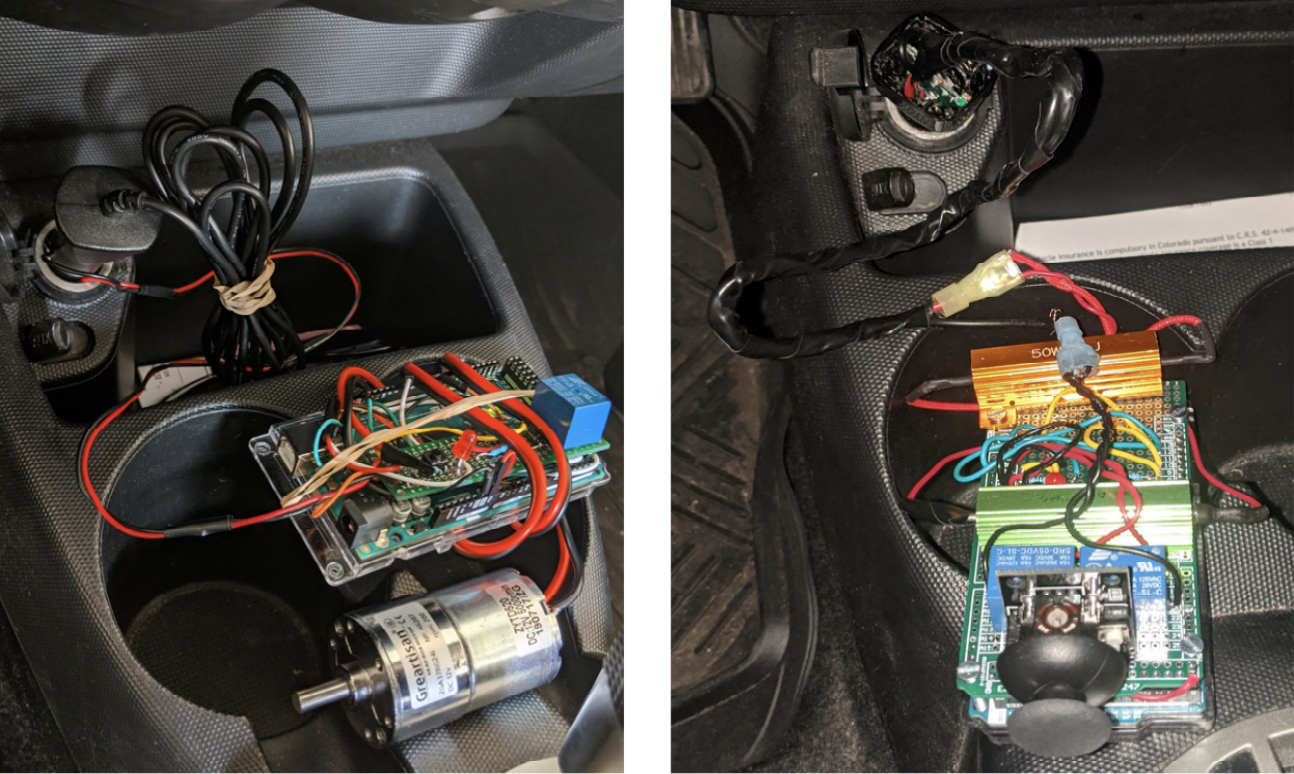
LibreCAN: Automated CAN Message Translator
CCS 2019Mert D. Pesé, Troy Stacer, C. Andrés Campos, Eric Newberry, Dongyao Chen, Kang G. Shin
LibreCAN can be used for automated translation of in-vehicle data, thus making the data flow in cars "transparent" to developers. In the future, we may be able to build apps on cars as easy as developing apps on smartphones!
Paper | Website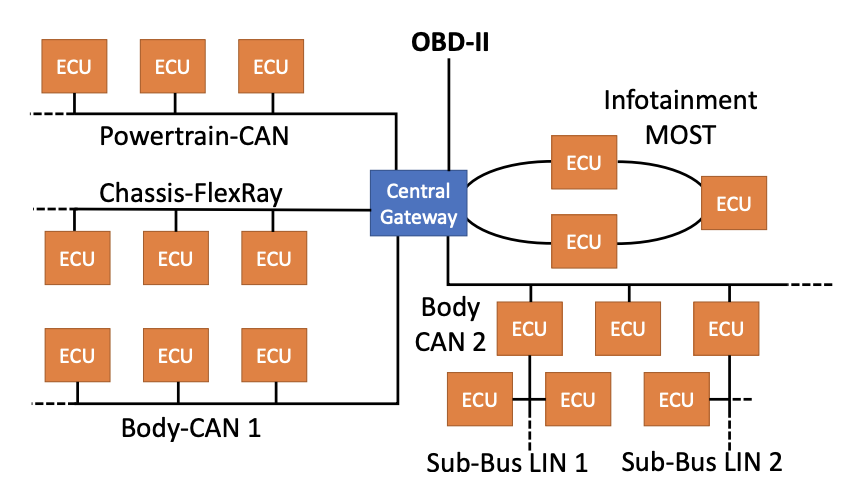
TurnsMap: Enhancing Traffic Safety with Crowdsensing and Deep Learning
UbiComp 2019Dongyao Chen, Kang G. Shin
This work presents TurnsMap, an IoT + AI framework for automatically detecting if a left turn is safe, e.g., whether it has protection for left-turning cars. Democratizing this information can help assure traffic safety for various transportation applications, e.g., navigation and ride-sharing apps.
Paper | Website | Slides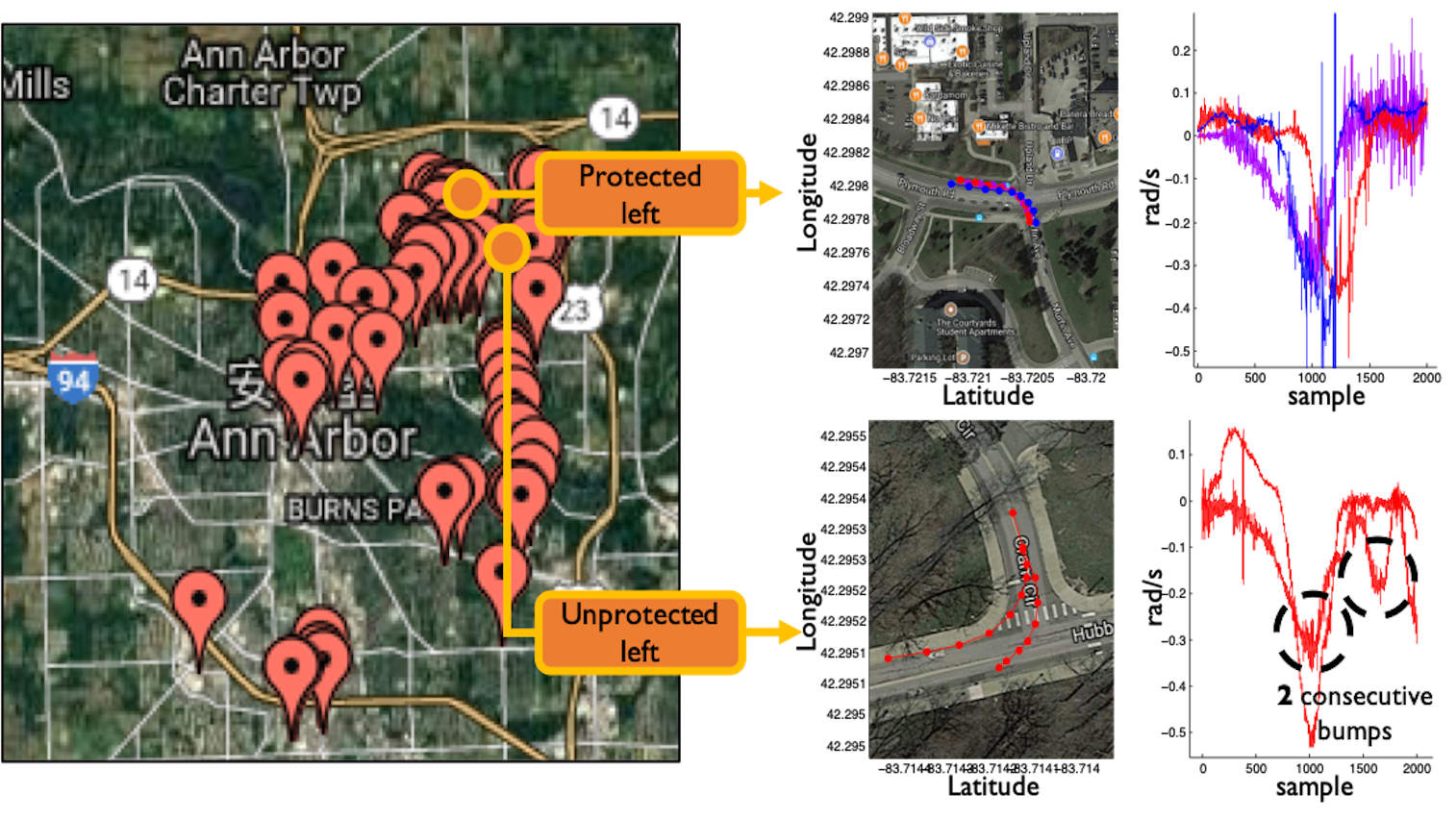
Mobile IMUs Reveal Driver's Identity from Vehicle Turns
ArXiv Preprint, 2017Dongyao Chen, Kyong-Tak Cho, Kang G. Shin
This work presents Dri-Fi, a solution that enables automotive apps to identify the person behind-the-wheel by only using mobile sensors. The capability of identifying driver is essential for personalized service/assistance for the driver and his/her designated parties, thus benefiting various automotive apps
Paper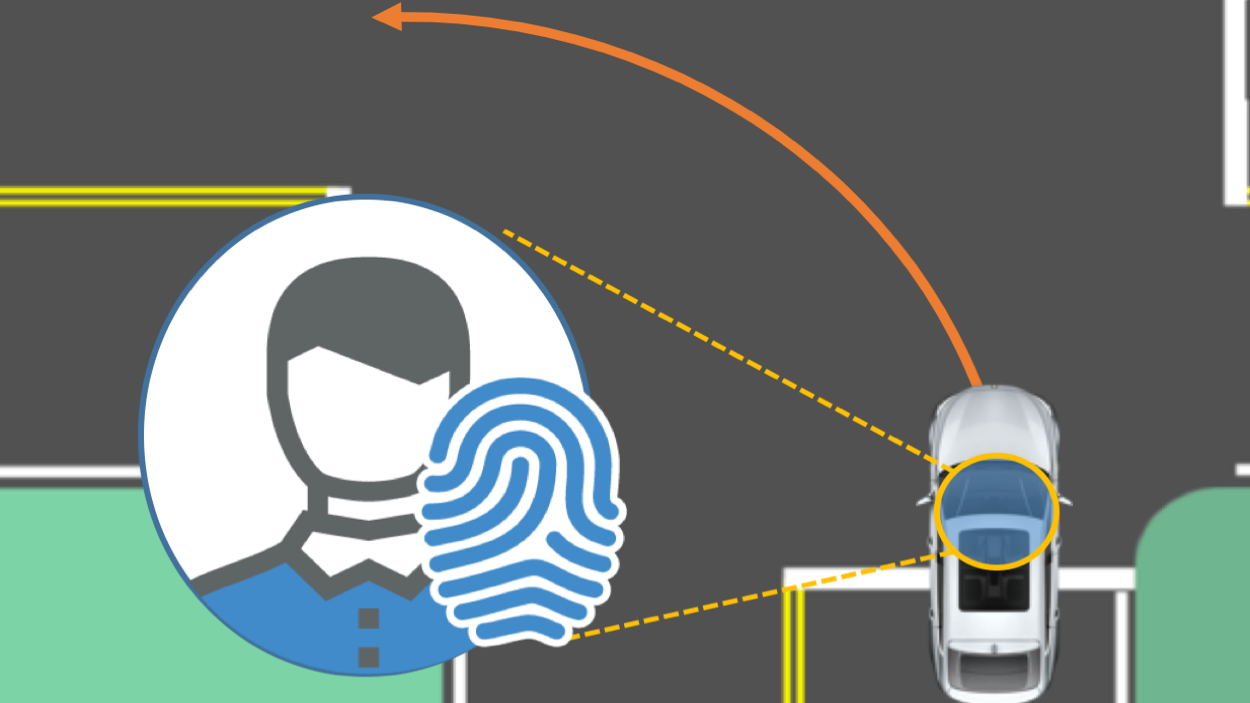
Locating and Tracking BLE Beacons with Smartphones
CoNEXT, 2017Dongyao Chen, Yurong Jiang, Kyu-Han Kim, Kang G. Shin
LocBLE is able to locate specific location of any surrounding Bluetooth low energy (BLE) beacons by justing using your smartphone. Comparing to existing coarse-grained BLE ranging applications, LocBLE is capable of enabling various use cases in Internet-of-Things. This is a collaborative work with Hewlett Packard Labs during my internship.
Paper | Demo | Slides
Invisible Sensing of Vehicle Steering with Smartphones
MobiSys, 2015Dongyao Chen, Kyong-Tak Cho, Sihui Han, Zhizhuo Jin, Kang G. Shin
This work introduced a vehicle steering detection middleware called V-Sense which can run on commodity smartphones without additional sensors or infrastructure support.
Paper | Demo | Slides
Vulnerability and Protection of Channel State Information in Multiuser MIMO Networks
CCS, 2014Yu-Chih Tung, Sihui Han, Dongyao Chen, Kang G. Shin
This work investigated vulnerability in MU-MIMO. Focusing on the plaintext feedback of estimated channel state information (CSI) from clients to the APs, we found that a malicious user could employ a sniff attack or a power attack by exploiting the vulnerability in the existing CSI feed scheme.
Paper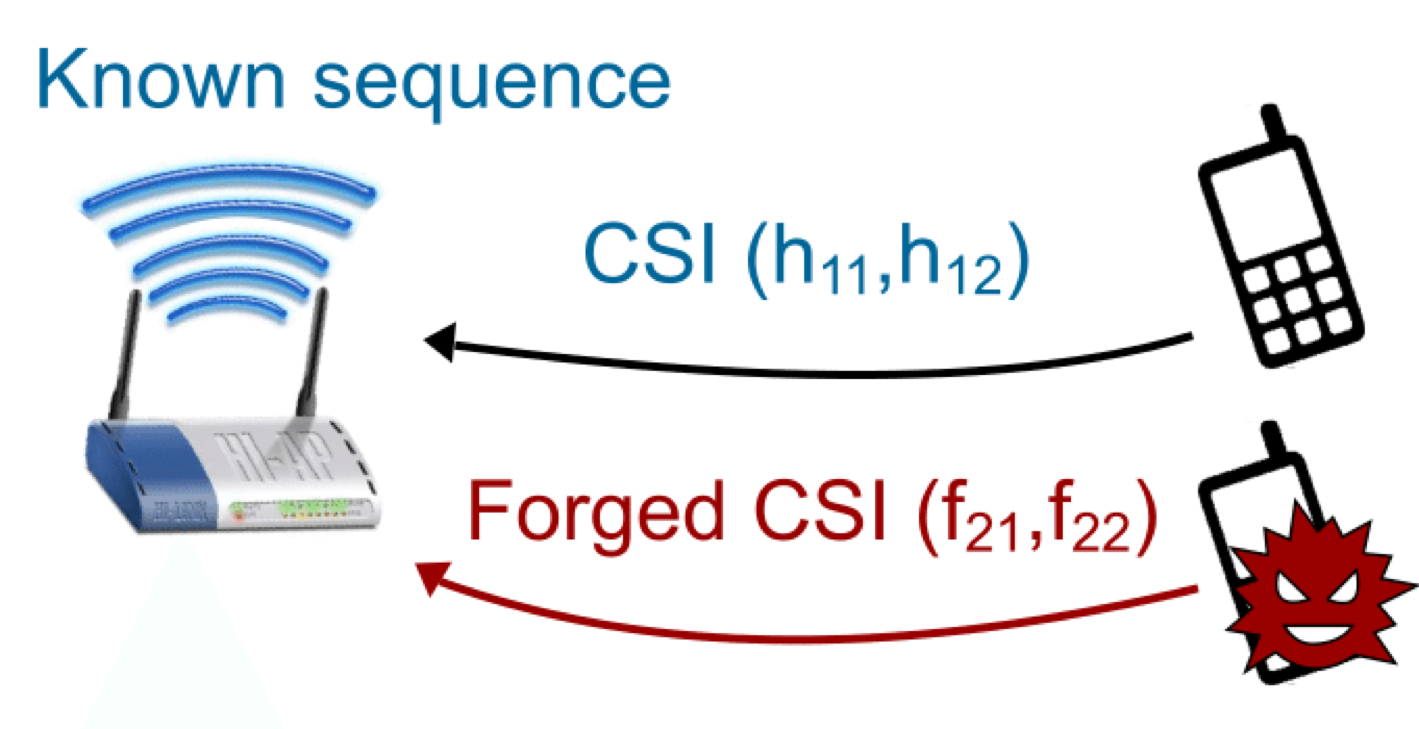
 chendy@sjtu.edu.cn
chendy@sjtu.edu.cn

















